- Forebrain (Telencephalon & Diencephalon)
- Diencephalon
- Hypothalamus
- Thalmus
- Cortex
- Sub-cortical areas
- Midbrain (Mesencephalon)
- Tectum & tegmentum
- Hindbrain (Metencephalon & Myelencephalon)
- Cerebellum & Pons
- Medulla oblongata
CNS:
- White matter = Tracts/Pathways (Columns = many tracts)
- Gray matter = Nuclei
PNS:
- White matter = Nerves
- Gray matter = Ganglia
31 Spinal nerves: "812551"
8 cervical
12 thoracic
5 lumbar
5 sacral
1 coccygeal
*Cervical spinal nerves exit from above the respective vertebra.
-Spinal nerve root 1 from above C1, and spinal nerve root 2 from b/w C1 and C2
-The rest of the spinal nerves (Thoracic, lumbar, etc.) emerge from below.
-Spinal cord ends at L1
Dorsal roots - Sensory fibers from dorsal root ganglia (DS)
-Carries afferent information
Ventral roots - Motor fibers from anterior gray column of spinal cord. (VM)
-Carries efferent information
Plexuses:
Cervical plexus (C1-C4)
-Innervate the muscles and skin of the neck and shoulder.
-Phrenic nerve supplies motor action of diaphragm. That's why neck injuries are so dangerous. Can cause respiratory arrest.
Brachial plexus:
Lumbar plexus:
Innnervates anterior and medial muscles of thigh.
---
Order of meninges:
Brain --> pia mater --> arachnoid membrane --> dura mater
Epidural injections are steroid injections used to reduce the inflammation and pain associated with nerve root compressions. Can be caused by herniated discs, spinal stenosis and etc.
---
Cranial Nerves:
I. Olfactory - Sense of smell
II. Optic - Sense of vision
III. Oculomotor - 4-6 muscles of eye (up & in), and contraction of pupil
IV. Trochlear - oblique muscle of eye (down & out)
V. Trigeminal - V1 opthalamic; V2 maxillary; V3 mandibular
VI. Abducens - Lateral rectus muscle of eye (abducts outwards)
VII. Facial - Facial expressions; anterior 2/3 tongue; salivary and lacrimal glands
VIII. Vestibulocochlear - Equilibrium & Hearing
IX. Glossopharyngeal - poterior 1/3 tongue; muscles of swallowing; senses carotid BP
X. Vagus - Senses aortic BP, slows heart rate,
XI. Accessory - Sternocleidomasteroid, trapezius, swallowing
XII. Hypoglossal - Innervation of tongue muscles
Locations in order, First 2 in Forebrain, second 2 in midbrain (brainstem), third 4 in pons (brainstem), last 4 in medulla (brainstem)
Tests:
Olfactory - sniff coffee beans
Olfactory - sniff coffee beans
Optic - Visual fields
Oculomotor - present eye with light for pupilary reflexes. Should move up & in. The eyes go down and out if there is a problem
Trochlear - Extraoecular movements. If eye can't go down & out, there is a problem
Trigeminal - light touch, plus corneal reflex, and clench teeth and open mouth against resistance.
Abducens - If eye doesn't abduct, problem. The patient will go cross-eyed. To compensate they will turn their head to avoid double vision.
Facial - Wrinkle forehead, smile, pucker, close eyes. Taste anterior 2/3 of tongue
Vestibulocochlear - Tuning fork
Glossopharyngeal - Gag reflex, tough, taste with posterrior 1/3 of tongue
Vagus - ??? Not in notes
Accessory - Rotate head and shrug shoulders against resistance
Hypoglossal - Stick tongue out straight
---
Sensory representation:
Modality - Receptor type to specific type of stimulus.
-Labeled line coding = Direct assocaition b/w a receptor and a sensation.
Location - Stimulation of a specific area defines the receptor's receptive field.
Location - Stimulation of a specific area defines the receptor's receptive field.
Intensity - Distinguished by frequency of AP's
-Number of receptors = population coding
-Frequency of AP's = frequencv coding
Duration - Time
Free dendritic endings - pain and temperature
Emcapsulated dendritic endings - nerve endings wrapped in connective tissue and serve as mechanoreceptors.
- Meissner's corpuscles - detect light touch
- Merkel discs - Also light touch like Meissner's corpuscles
- Krause's End bulbs - detect fine touch in mucus membranes
- Pacinian Corpuscles - Deep connective tissue, respond to vibration and deep pressure
- Ruffini's Corpuscles - Found in dermis to respond to continuous pressure
Tonic receptors - Adapt slowly or do not adapt at all.
-Ex: Muscle stretch receptors, joint proprioceptors
CNS must continually get info about degree of muscle length and joint position.
Phasic receptors - Rapidly adapting receptors
-Ex: Tactile receptors in the skin
Don't respond to maintained stimulus
---
Motor fiber types
Sensory fiber types:
___________________________________________________________________________________
Proprioceptors: Provide information about joint angle, muscle length & tension.
- Skeletal muscles, joints tendons, ligmaents
- Muscle spindles
- Golgi tendon organs
- Joint kinesthetic receptors
Ia sensory fibers = Annulospiral endings, muscle spindles (found throughout skeletal muscle)
II sensory fibers = Flower-spray endings, golgi tendon organs
Only type IV sensory fibers are unmyelinated
-Gamma efferent motor fibers let the brain preset the sensitivity of the spindle to stretch.
Muscle spindles detect changing length of muscle via contractions and stretches.
Pain, temperature, coarse touch, tickles and itches cross the spinal level. Fine touch and pressure crosses at the medullary level.
---
Glutamate binds AMPA and NMDA resulting in AP, which transmit signals to higher centers.
Lateral spinothalamic - pain and temperature (cross at spinal cord)
Ventral (anterior) spinothalamic - coarse touch, tickle or itch (cross at spinal cord)
Medial lemniscus pathway - find touch, pressure (cross at medulla) (dorsal column)
Conscious proprioception - Communicated by posterior column-medial lemniscus pathway.
Unconscious proprioception - Communicated by dorsal spinocerebellar tract, to the cerebellum.
Ascending and descending tracts in the white matter of the spinal cord in cross section:
Major Ascending pathways for somatic senses:
Spinocerebellar - proprioception from skeletal muscle to cerebellum of same side (don't cross)
Dorsal Column - Discriminative touch sensation through thalamus to somatosensory cortex (cross in medulla)
Spinothalamic - Nondiscriminate sensations (pain, temp pressure) through the thalamus to the primary somatosensory cortex (cross in spinal cord before ascending)
Some Descending pathways:
Pyramidal tracts:
Lateral corticospinal - cross in pyramids of medulla; voluntary motor to limb muscles
Central corticospinal - cross at spinal cord' voluntary to axial muscles
-----
E = CS^2 where S = Body weight, and C = Cephalization factor, and E = brain weight
-----
Reflexes:
Rooting - reaction when infant's cheek is stroked
Moro reflex - startle response in reaction to sudden intense noise or movement
Grasping reflex - obvious
Sucking reflex - obvious
-----
Eyes open = Beta waves
Eyes closed = alpha waves
Sulcus - Groove and line
Gyrus - Hill and bump
Central sulcus - separates frontal and parietal loves.
-----
Cerebral cortex:
Supplementary motor area - Complex patterns of movement (opening or closing hand)
Premotor cortex - Important in orienting the body and arms toward a specific target
Posterior parietal cortex - Lies posterior to primary somatosensory cortex
-If damaged, cannot process complex sensory information to accomplish purposeful movement.
Broca's area - in frontal lobe
Wernicke's area - in temporal-parietal lobes
Circumventricular organs - Parts of the brain that lack a BBB
Pericytes - contractile cells that wrap around the endothelial cells of capillaries throughout the body. Allow the cells to regulate capillary blood flow.
-----
Membrane equilibrium for potassium = -90mV
Membrane equilibrium for sodium = +60mV
-----
Conduction speed of electricity through neurons is proportional to square root of the diameter.
Increasing diameter = Increase conduction velocity
Decrease capacitance (through myelination) = Decrease amount of energy it takes to depolarize a membrane.
-----
Tests to diagnose Multiple Sclerosis include lumbar puncture, including CSF oligoclonal banding. Also an MRI scan of the spine.
---------------------------
Kinesin + Dynein = Fast axonal transport
Astrocytes take up and degrade glutamate and GABA. They also take up excess K+ from brain ECF.
Microglia release nerve growth factor which helps neurons and glial cells survive.
-----
___________________________________________________________________________________
NT's made from tyrosine = Dopamine, Noradrenaline, Adrenaline
NT's made from tryptophan = Serotonin, Histamine
Parkinson's disease - deficiency of dopamine
Schizophrenia - dopamine receptor abnormalities
Norepinephrine though to be involved in etiology of bipolar affective disorders
1. Glutamate - Excitatory
- Ionotropic
- NMDA receptors (high permeability to Ca+)
- Important in learning in memory
- Neurotoxic if present in high doses for a long period of time.
- Neurons literally stimulated to death.
- AMPA is a non-NMDA-type ionotropic transmembrane receptor for glutamate
2. GABA - Inhibitory
- Selectively permeable to Cl-
- Benzodiazepines, barbiturates and alcohol augment effect.
- Decrease GABA inhibition = epilepsy
Neuropeptides:
Substance P - Transmits pain.
Neuropeptide Y - Stimulates appetite and food intake
NO and CO activates guanyl cyclase and cGMP
H2S is a neuroprotectant against oxidative stress. It shows cardioprotective effects.
*Nicotinic receptor = Excitatory at neuromuscular junctions with skeletal muscle
*Muscarinic receptor = Inhibitory in cardiac muscle
Ionotropic receptors:
- Ion channels
- Nicotinic receptors
- Minimal amplification
- Rapid
- Glutamate and GABA act through these
Metabotropic receptors:
- G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs)
- Muscarinic receptors
- Large amplification
- Not rapid
- Neuropeptides and biogenic amines act through these
Nicotine is an ACh agonist (ionotropic)
Curare is an ACh antagonist, and causes paralysis (ionotropic)
Muscarine mimics ACh (muscarinic)
Atropine blocks ACh (muscarinic)
Two types of muscarinic receptors:
M2: heart; opens K channels to hyperpolarize
M1: intestine; closes K channels to depolarize
---
Adrenergic receptors
alpha-receptor response = vasoconstriction
beta-receptor response = vasodilation
Opioid receptors belong to a family of 7 transmembrane GPCRs
To get rid of ACh = acetylcholinesterase
To get rid of Norepinephrine = MAO (monoamine oxidase)
Ion channels = fast EPSP
GPCRs = slow EPSP
Presynaptic inhibition = inhibits some response
Postsynaptic inhibition = inhibits all response
Long-Term potentiation (LTP) = Activity at a synapse induces sustained changes in quality or quantity of connections . Glutamate is key element in potentiation since it's the main excitatory NT.
Myasthenia gravis (PNS) - Severe weakness of the muscle. Functional disorder at the synapse b/w the motor neuron and skeletal muscle.
-Antibodies block or reduce number of nicotinic ACh receptors
Parkinson's (CNS) - Decreased stimulation of motor cortex by the basal ganglia. Insufficient formation of dopamine
Schizophrenia (CNS) - Increased dopamine activity in mesolimbic pathway
-Benzodiazepines facilitate GABA binding
-Agonistic action of GABA may account for the sedative-hypnotic and anesthetic properties.
___________________________________________________________________________________
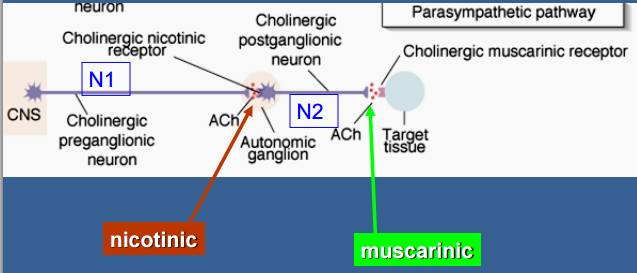
Sympathetic Nervous System = T1-L2
Parasympathetic Nervous System = Cranial nerves III, VII, IX, X and emerge from sacral at S2-S4
Parasympathetic = ACh
Sympathetic = Norepinephrine
Sympathetic = Long post-ganglionic neurons, postganglions release into adrenergic receptors, however, preganglions secrete ACh
Parasympathetic = Long pre-ganglionic neurons, postganglions release ACh, preganglions secrete ACh also
ACh is made from acetyl-CoA and choline
Catecholamines are made from phenylalening and tyrosine, in that order
Reserpine is a drug that blocks the transport of dopamine into vesicles.
Nicotinic receptors = found on postganglionic cell bodies of all autonomic ganglia.
Muscarinic receptors = found on effector cell membranes.
---
Adrenergic receptor systems
Beta 1 = heart, adipose tissue, Renin release from JG cells
Beta 2 = vascular smooth muscle, airway smooth muscle
Muscarinic receptors - cardiac conduction system and exocrine glands and smooth muscles in PNS
-In CNS, sweat glands
Termination of NT activity - through COMT and MAO.









No comments:
Post a Comment